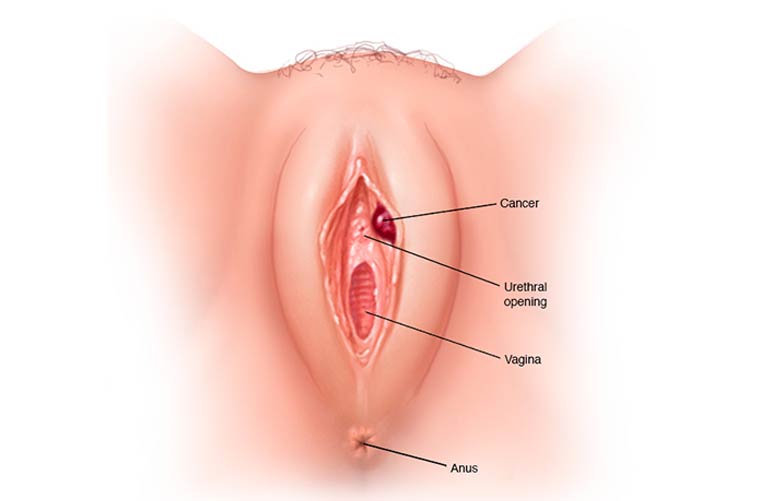
Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer is a form of cancer that develops on the female genitalia's outer surface. The vulva is the skin that covers the urethra and vagina, as well as the clitoris and labia.
Vulvar cancer typically manifests as a lump or sore on the vulva, which causes itching. Vulvar cancer can occur at any age, but it is most usually diagnosed in elderly people.
Surgery to remove cancer and a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue is frequently used to treat vulvar cancer. Vulvar cancer surgery may necessitate the removal of the entire vulva. The earlier vulvar cancer is detected, the less likely it will require significant surgery for treatment.
Symptoms
- Itching that will not go away.
- Tenderness and pain
- non-menstrual bleeding Skin changes, such as color changes or thickening,
- A lump, warty pimples, or an open wound
Who gets vulvar cancer?
- Have vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia
- Have human papillomavirus infection.
- Have a history of genital warts.
- Have a skin condition involving the vulva, such as lichen sclerosus.
- Older people
- Having many sexual partners
- Having a history of abnormal Pap tests
- Having a medical condition that weakens your immune system
- Being a smoker
