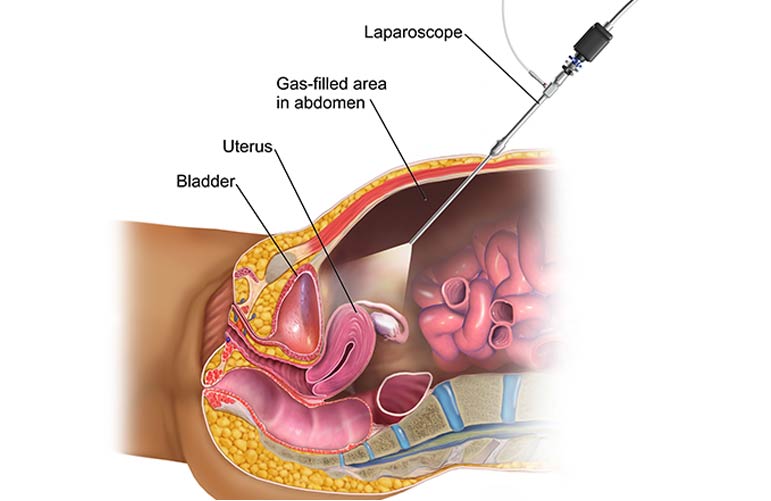
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
A laparoscope is a type of medical telescope. It is linked to bright light and a high-resolution monitor. A hollow tube is implanted through your abdominal wall to allow the surgeon to look within your belly, and the laparoscope is introduced into the port. The monitor then displays a view of the inside of your abdomen. In most circumstances, this technique will be able to diagnose or assist in determining the cause of the stomach ailment.
Why is diagnostic laparoscopy performed?
Abdominal pain
Laparoscopy can be used to diagnose both acute and persistent abdominal pain. Abdominal pain can be caused by a variety of factors. Appendicitis, adhesions or intra-abdominal scar tissue, pelvic infections, endometriosis, abdominal hemorrhage, and, less frequently, malignancy are among the reasons. It is used to rule out alternative causes of stomach pain in people with irritable bowel syndrome. Surgeons can frequently determine the source of stomach pain and fix it during the same procedure.
Abdominal mass
A lump can be felt by the doctor, visible on an X-ray, or felt by the patient. Before suitable therapy or treatment can be offered, most masses require a clear diagnosis. Laparoscopy is one of the techniques accessible to your doctor to examine the mass directly and retrieve tissue to determine the diagnosis.
Ascites
Ascites are the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The cause of this fluid collection cannot always be determined without peering into the abdominal cavity, which is often possible via laparoscopy.
Liver disease
Ultrasound, CT scan (computed tomography), and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are non-invasive imaging procedures that can detect a mass inside or on the surface of the liver. If non-invasive imaging does not provide your doctor with enough information, a liver biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis. Diagnostic laparoscopy is one of the most precise and safe methods of obtaining tissue for diagnosis. In other words, it is a precise method of collecting a biopsy to sample the liver or a mass without having to open the abdomen.
Cancer staging
Your doctor may require information about the progress of a previously treated disease, such as cancer. This can happen after some types of chemotherapy or before more chemotherapy is started. Additionally, diagnostic laparoscopy may provide information prior to planning a formal investigation of the abdomen, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
What tests are necessary before laparoscopy?
Your doctor may order an ultrasound as a non-invasive diagnostic exam. In many circumstances, information is provided that will help your surgeon understand the problem inside your abdomen. This test is not uncomfortable, is highly safe, and can improve the diagnostic laparoscopy's performance.
CT Scan is an X-ray that employs computers to visualize the contents of the abdomen. It is accurate in diagnosing abdominal illness in certain instances. It will provide your surgeon with a "road map" of the interior of your abdomen. A CT scan may be used by a radiologist to insert a needle into your abdomen. This is referred to as a CT-guided needle biopsy.
