Tubal Ligation
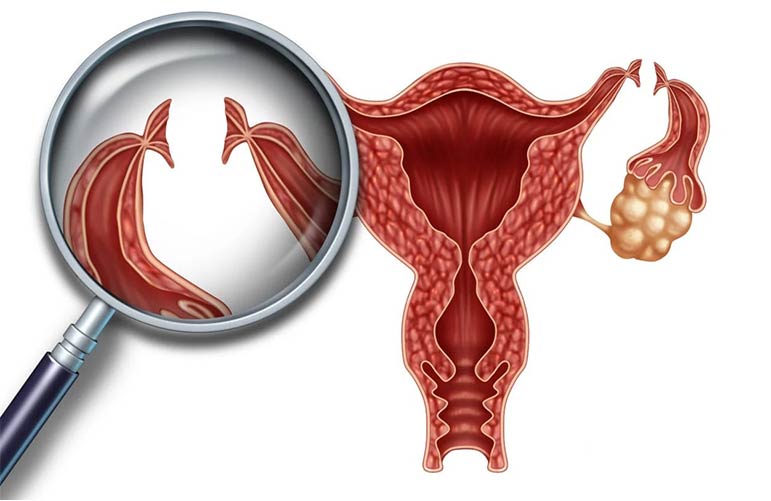
A tubal ligation (sometimes known as "tying your tubes") is a treatment that closes both fallopian tubes, preventing sperm from reaching an egg to fertilize it. Rings, clips, or cutting and tying are used to shut the tubes.
Typically, a tiny telescope called a laparoscope is inserted through a small cut around the belly button, and the tubes are closed through another small cut near the pubic hair. If a laparoscope cannot be used, a longer cut near the pubic hair is made.
Tubal ligation, also known as having your tubes tied, is a type of female permanent sterilization. It occurs when a woman's fallopian tubes, which transport an egg to the uterus each month, are surgically obstructed or closed.
This stops the egg from ever being fertilized by sperm, resulting in pregnancy. It is for ladies who are confident that they do not wish to become pregnant or have children following the operation.
Tubal ligation is a surgical technique that is used to prevent pregnancy. It's usually referred to as "having your tubes tied." Female sterilization is another term for it. The fallopian tubes are referred to as tubal. Every month, an egg is released from an ovary and goes to the uterus via the fallopian tube. Ligation is a verb that implies binding. This prevents the egg and male sperm from forming a connection, thereby preventing pregnancy.
Both fallopian tubes are blocked or cut during this surgery. It is typically performed in a hospital or an outpatient surgical clinic. In most circumstances, you will be able to leave the hospital the same day. This procedure can be performed under general anesthesia, local anesthesia, or spinal anesthesia.
You will still have your periods and have sex after the operation. In fact, because they do not have to worry about an unexpected pregnancy, women may feel more at peace. Tubal ligation is a permanent method of birth control. Although it can be corrected with another operation, only around half to eighty percent of women who have their fallopian tubes reattached are able to become pregnant. This procedure does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases. You must continue to practice safe sex.
