Ovarian And Tubal Surgery
The fallopian tube and ovary are well located in the pelvis, practically all surgeries for nonmalignant disorders with these organs are best performed laparoscopically. Adnexal surgery includes the following procedures:
- Ovarian cystectomy - The removal of an ovarian cyst while the ovary is preserved.
- Oophorectomy is the surgical removal of the ovary.
- Salpingectomy is the surgical removal of the Fallopian tube.
- Salpingotomy - The opening of the tube to remove an anomaly, such as an ectopic pregnancy.
- Adhesiolysis is the removal of adhesions from the tube or ovary in order to relieve pain or promote fertility.
Many of these procedures can be completed in a single day. It is vital to discuss your recuperation requirements with your doctor to achieve the best possible strategy for you.
Advantages
- Smaller incisions and scarring
- increased visibility of the tubes and ovaries
- Gentler handling of bodily tissues and organs during surgery
- Less blood loss during the procedure
- Postoperative pain is reduced.
- Postoperative opioid pain treatment is used less frequently.
- Hospitalization time is reduced.
- Faster overall healing and return to normal activity
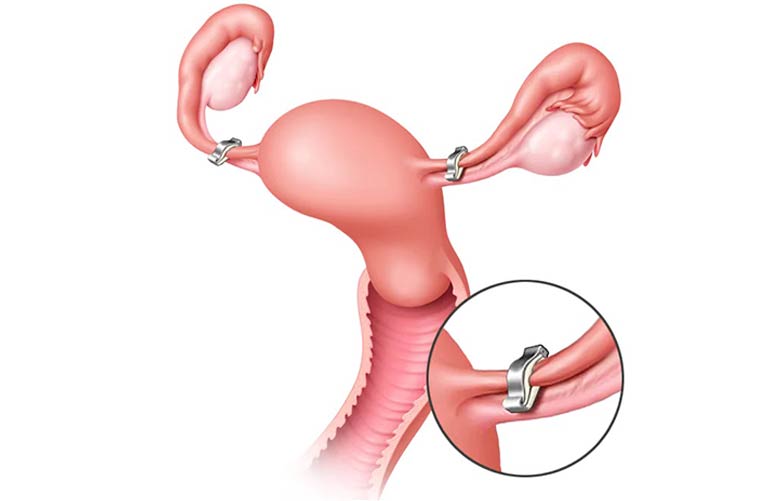
Tubal ligation, often known as tubal sterilization or having your tubes tied, is a kind of permanent birth control. Tubal ligation permanently prevents pregnancy by cutting, tying, or blocking the fallopian tubes.
Tubal ligation prevents an egg from passing from the ovaries to the fallopian tubes and also inhibits sperm from passing from the ovaries to the egg. Your menstrual cycle is unaffected by the surgery.
Tubal ligation can be performed at any time, including after childbirth or as part of another abdominal surgery, such as a C-section. Most tubal ligation operations are irreversible. If a reversal is tried, it necessitates extensive surgery and is not usually successful.
One of the most popular surgical sterilization procedures for women is tubal ligation. Tubal ligation permanently prevents conception, eliminating the need for birth control. It does not, however, protect against sexually transmitted illnesses.
Tubal ligation may also reduce your chances of developing ovarian cancer, particularly if the fallopian tubes are removed. However, tubal ligation is not for everyone. Consult your doctor or health care provider to ensure you fully understand the procedure's dangers and advantages.
